Fungal infection in debilitated or inmunosuppressed patients or during broad-spectrum antimicrobial terapy are frequent.
Candida species are the most common fungal pathogens Candida Albicans is by the most frequent cause of clinically significant infections esophagitis.
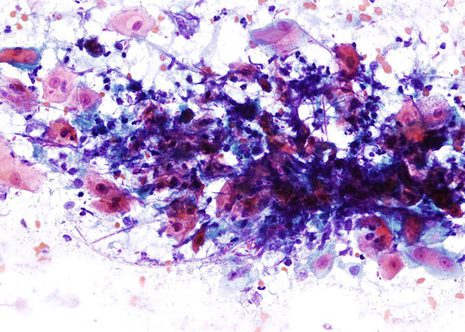
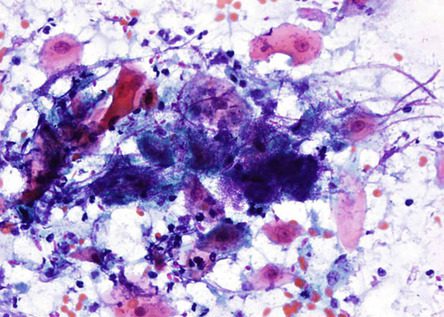
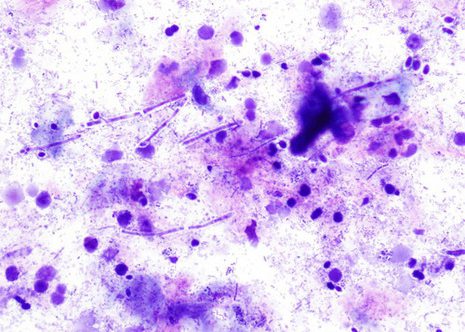
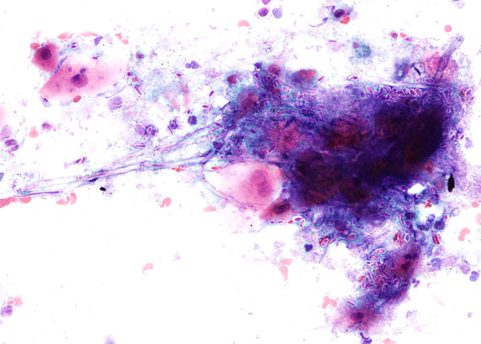
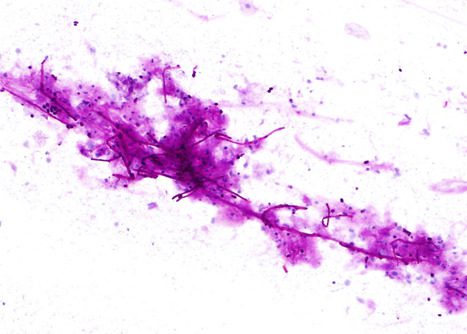
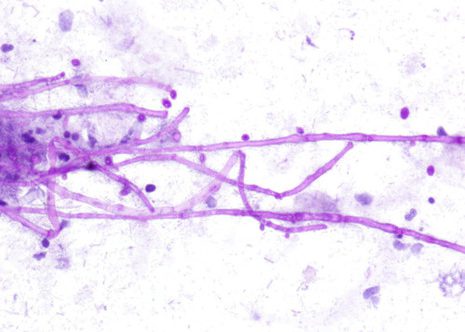
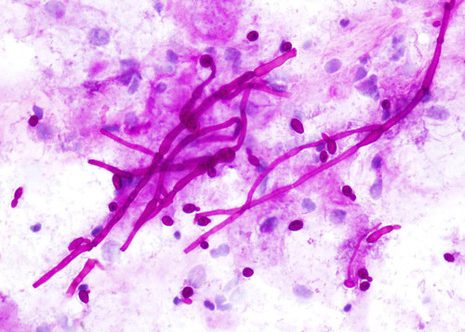
Candida typically produces a pseudomembrane that covers and is attached to the squamous mucosa.
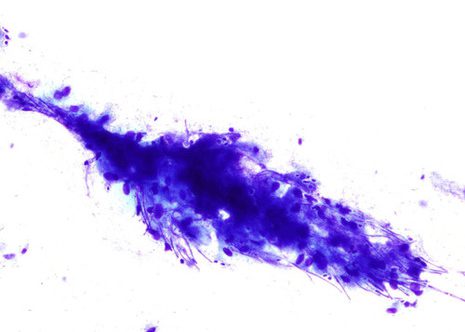
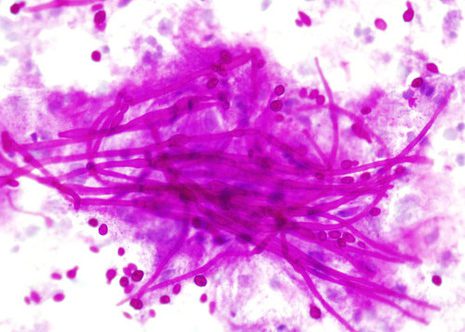
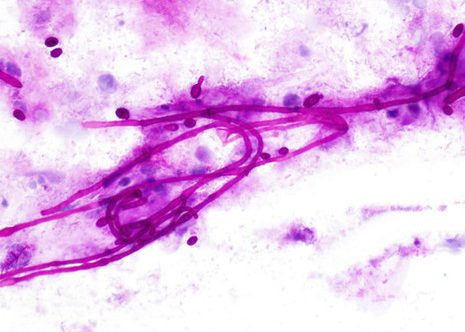
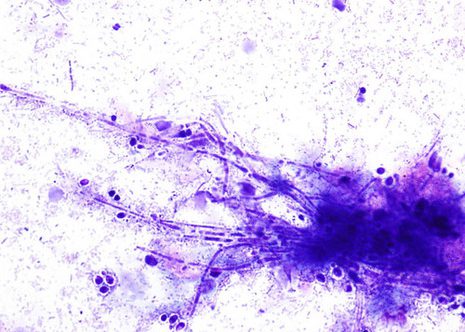
Candida pseudohyphae and spores are relatively common findings in brush smears in the presence of fungal esophagitis.
The images correspond to the cytology by esophageal brushing of a man of 43 years with fungal esophagitis.